Printing is a process for reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest examples include Cylinder seals and other objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The earliest known form of woodblock printing came from China dating to before 220 A.D. Later developments in printing include the movable type, first developed by Bi Sheng in China. The printing press, a more efficient printing process for western languages with their more limited alphabets, was developed by Johannes Gutenberg in the fifteenth century.Modern printing is done typically with ink on paper using a printing press. It is also frequently done on metals, plastics, cloth and composite materials. On paper it is often carried out as a large-scale industrial process and is an essential part of publishing and transaction printing.
- Digital Printing - Desktop printers are important to desktop publishing. It was primarily the introduction of both the Apple LaserWriter, a PostScript desktop printer, and PageMaker for the Mac that kicked off the desktop publishing revolution.
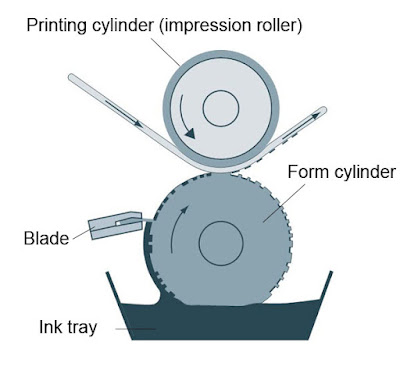
- Offset Lithography - Lithography is an "offset" printing technique. Ink is not applied directly from the printing plate (or cylinder) to the substrate as it is in gravure, flexography and letterpress. Ink is applied to the printing plate to form the "image" (such as text or artwork to be printed) and then transferred or "offset to a rubber "blanket". The image on the blanket is then transferred to the substrate (typically paper or paperboard) to produce the printed product.
- Gravure Printing - Rotogravure (roto or gravure for short) is a type of intaglio printing process, which involves engraving the image onto an image carrier. In gravure printing, the image is engraved onto a cylinder because, like offset printing and flexography, it uses a rotary printing press.
- Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics (and moderate-quality photographs) by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylindrical drum to define a differentially-charged image.



No comments:
Post a Comment